A peculiar photo surfaced a few weeks ago from Canada: a distant message to Hungarians from 1956, taken from an American aircraft carrier. On the deck, the crew forms huge letters, and the Yankee sailors come together to create a Hungarian-language inscription: “Isten segítsen” (God help you). What could be the story behind this image, and who is the unknown sailor who initiated the Hungarian message from the deck of the USS Coral Sea? Solidarity, a prayer, a tribute to a revolution left to fend for itself – one of the 200,000 refugees from 1956 donated the 200,000th photo to Fortepan.
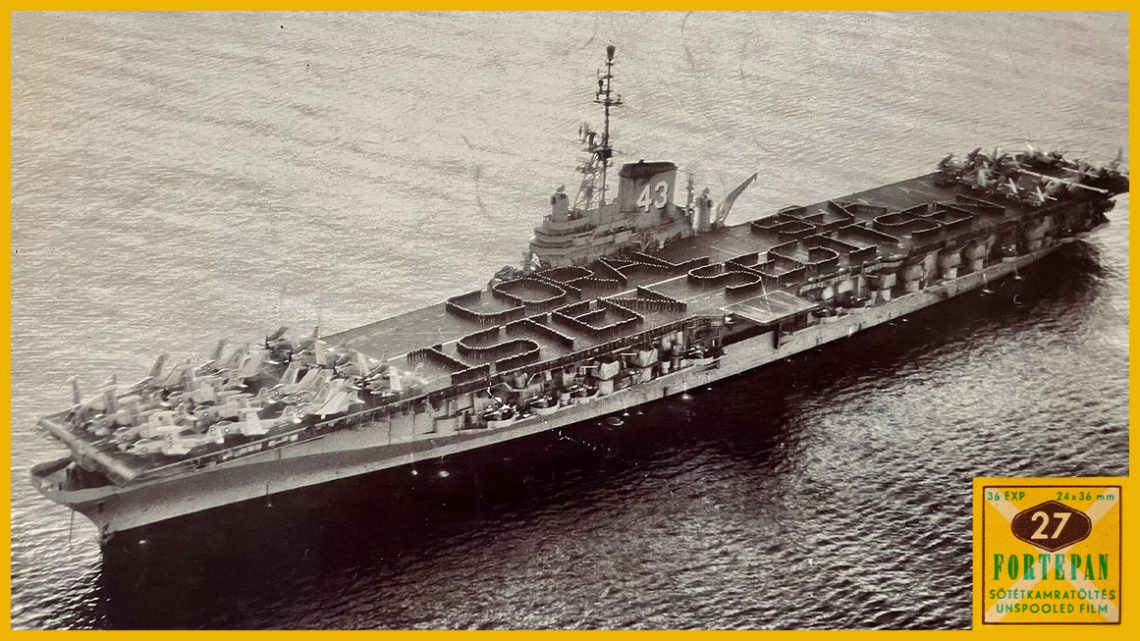
Instead of a series of images, this time only a single photograph appears in the Fortepan selection, and notably, this photo is the 200,000th piece in Hungary’s private photo album. The shot was likely taken at the end of 1956 or early 1957, depicting an American aircraft carrier anchored off Naples from a bird’s-eye view. On the USS Coral Sea, sailors stand in a special formation among military planes, spelling out the Hungarian-language message: “Isten segítsen” (God help you).
The Coral Sea was one of the large Midway-class aircraft carriers of the U.S. Navy. Its history spans the Cold War period: it was launched in 1947, the year Hungary was Sovietized, and although it bore the nickname “Ageless Warrior,” it was decommissioned in 1990, the year of the regime change. In the 1950s, it spent most of its time in the Mediterranean, and apart from this image, it had few Hungarian connections.
At the end of October 1956, during the days of the Hungarian Revolution, it was deployed to the Middle East due to another major global event—the Suez Crisis—which partially diverted Western public attention from Hungary to evacuate American citizens from Alexandria and Haifa.
According to recollections, there was also a Hungarian-American sailor serving on the Coral Sea—perhaps as a helmsman. He was likely the one who suggested that the money originally collected as a Christmas gift for the crew be donated to help Hungarian refugees instead. This initiative was signed by everyone on the aircraft carrier, and a total of $7,500 was offered to the fund aiding the refugees.
It is possible that he also proposed that the crew form the huge Hungarian-language message on the deck. However, we do not know the name or story of the Hungarian sailor. If anyone has information about him, we would appreciate it if they wrote to us; perhaps together we can piece together the unknown fragments of this story.
The American foreign policy also sought to capitalise on the striking gesture of solidarity with Hungary, the crushed revolution, and the Hungarian refugees. The aerial photo may have been taken for this reason: copies of the photo were circulated among the Hungarian refugees, and even trips were organised for them to Naples to see the aircraft carrier.
This photograph eventually reached a 13-year-old Hungarian boy. I. Béla Barabás was an eighth-grade student when he left Hungary with his family in December 1956. Béla’s family lived in Tósokberénd, near Ajka, during the revolution. His father previously worked as an agronomist in Rákosi’s era’s major agricultural experiment, focusing on the introduction of cotton cultivation in Középhídvég, Tolna County.
However, he was unwilling to join the party even when persuaded, and when the cotton project failed, he also had to leave, leading the family to move to Veszprém County. During the revolution, the family held a vote: involving the children, they voted on whether to leave or stay. His father and brother voted to leave, while his mother and sister voted to stay in Hungary, so ultimately, Béla’s vote decided the outcome, and he chose the adventure.
Initially, they only made it to Győr, where his mother suffered a nervous breakdown while waiting for their transfer.
“We’re leaving our whole life behind, we don’t even know which country we’re going to, and we don’t speak the language.”
They returned home, but a week later, they set off again towards the Austrian border.
“Everyone brought a small bag; one contained family photos, but we could hardly take anything with us.”
— said I. Béla Barabás, a retired landscape architect from Saskatoon, Canada
In November, it was still easy to cross the border, but by mid-December, when they finally made up their minds, the situation was no longer so simple.
“My father didn’t want to go with a large group, so we set off alone from Sopron. It was seven in the evening, and there was a curfew. Someone offered to help us cross for money. We gave him what we had; I remember he smelled like alcohol. ‘Follow this path; Austria is that way,’ he said, more or less, and then we parted ways. The path ended soon; there was mud and rain, and we walked in the dark until three in the morning. We heard dogs barking, and from a distance, machine guns firing, but after a while, we encountered a border guard who spoke German. We made it across.”
This was the main route for emigration in the last weeks of 1956. By the time the Barabás family made it out, Austria was practically full, and the refugee camps were packed. By then, the background agreement had been established that Austria would only serve as a “first refuge,” and the long-term accommodation would be taken on by other countries.
The 13-year-old Béla’s most vivid memory from their three-day stay in Austria was that he received a pocket knife as a gift—his first personal knife. From Vienna, they were taken by closed train to Rome, where they stayed until May 1957.
There weren’t many Hungarians in Italy yet; the first arrivals caused quite a sensation, and interview crews were everywhere.
It is said that 1956 was the world’s first revolution broadcast live, and among the foreign correspondents bustling in Budapest, there were also Italians.
Indro Montanelli, a star journalist who had covered every front from Abyssinia to World War II, reported with great enthusiasm for the Corriere della Sera about the events, recognising that the fate of the revolution, which was believed to be victorious for a few days at the end of October, was very unstable, as Soviet troops, contrary to their promises, were not withdrawing and were preparing to attack.
“I am already a fairly seasoned war correspondent, and—believe me—I have seen everything. I have never had the feeling that I was encountering heroic tales, except for a few rare individual episodes, and I always thought such things did not exist as a collective phenomenon. I was wrong. They exist. At least in Hungary.”
— he wrote from Budapest.
After the revolution was crushed, there was immense sympathy for Hungarians in Italy. Even the Catholic pontiff—Pope Pius XII—issued three encyclicals during the days of the revolution, welcoming the refugees. “Viva papa, viva papa!” — I. Béla Barabás heard from all around; he himself recalls being welcomed with open arms in Italy. For him as a child, it was primarily a huge adventure. TV cameras, the sea, and once even Puskás Öcsi, who also found his way to Italy, appeared in an open car surrounded by a cheering crowd.
The family was first placed in an evacuated orphanage. Four to five families lived together in one room, but the food was good, and the children enjoyed the experience of regularly receiving tropical fruits. Béla sold some of them for a few lira to Italian kids—the money was spent on movies, where he watched American cowboy films.
For the children, it was essentially a golden life. Plenty of free time, roaming around Rome unsupervised, and new impressions of adult life: peeking at couples making out in tiny Fiat 500s; witnessing the public humiliation of three Hungarian women who resorted to prostitution being shaved bald in the refugee camp—all while an Italian nun tried to teach them the language, primarily through prayers.
After three months in the overcrowded orphanage, the Barabás family moved to much better conditions, an old Roman palazzo. Although he remembers it as the Hungarian embassy, it was probably the Falconieri Palace on the banks of the Tiber, where the Collegium Hungaricum once operated.
The Hungarian political police left the building during the days of the revolution, which made it available, and with the help of the Papal Hungarian Church Institute, Hungarian refugees were placed there; it became a temporary home for many Hungarian university students and professors. Béla’s mother got a job in the kitchen, allowing the family to move into the 16th-century palace, and Béla was able to peel potatoes in the kitchen alongside Vera Pásztor, the famous dancer from the Budapest Opera House.
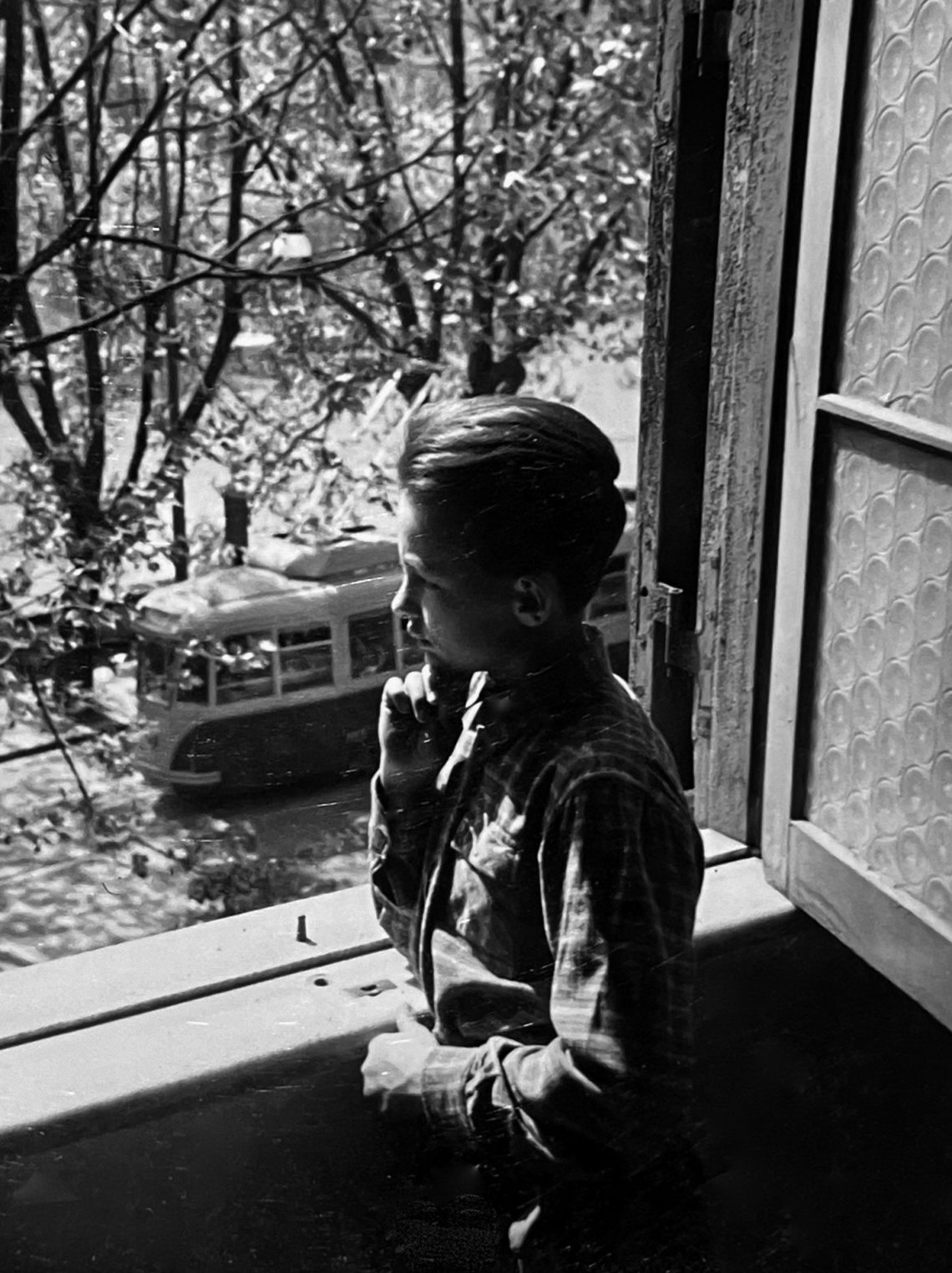

All of this was a transitional period before the Hungarian refugees moved on to their final host country from Italy. In the meantime, they tried to make the most of their time, so there was great enthusiasm when they received an invitation to Naples from the Americans.
One day, his father came home with a photo of the ship, announcing that a Hungarian was the helmsman, and that they had offered a free bus trip to the port of Naples. Only adults could go, but everyone was very excited about the opportunity to see something special. Everyone was surprised that the helmsman was able to convince the sailors to write: “Isten segítsen.” This was received with great gratitude by the people.
This grassroots initiative was one of many spontaneous gestures of solidarity that manifested throughout the Western world regarding the Hungarian Revolution during those weeks. The message in the photographs that could be reproduced also fit well into the political narrative of the time, which greatly sought to support those who fled, trying to help the Hungarian refugees as much as possible.
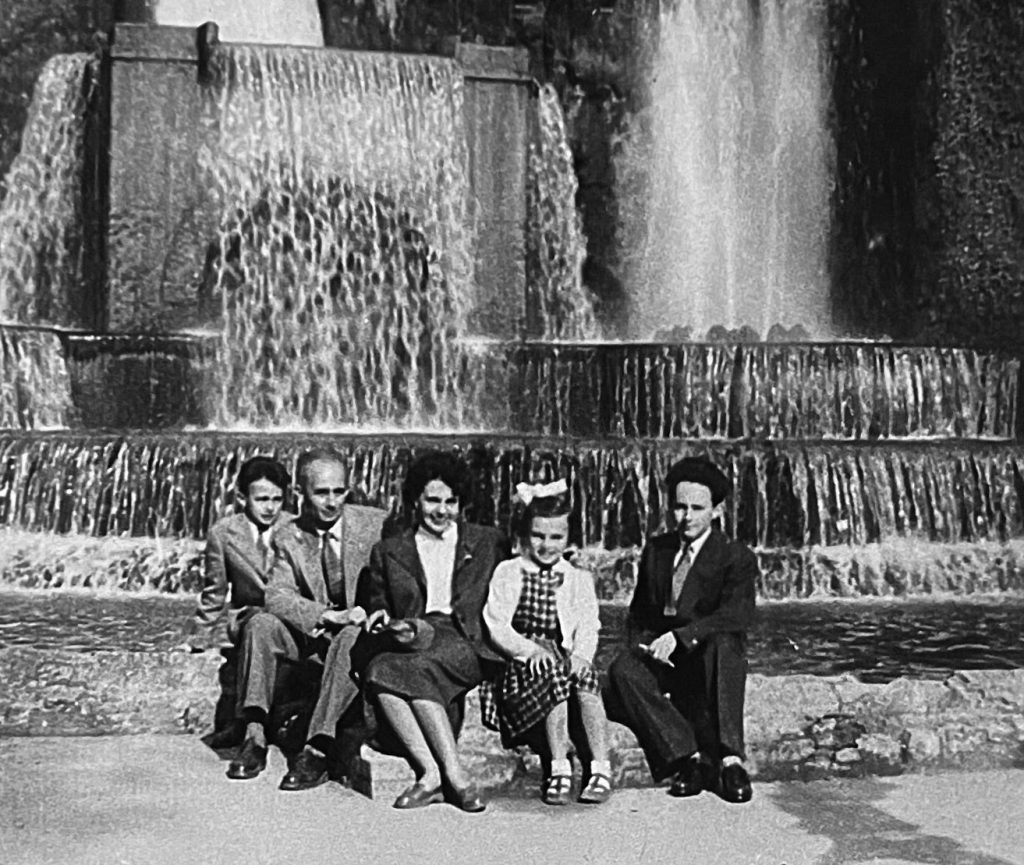
Not only were the days filled with opportunities for the young Béla to venture to the seaside, but he also got to know the American soldiers stationed in Italy, whom he described with a childlike candour as “the biggest cowboys.” Many had come to Europe through the Marshall Plan and decided to stay for several years. They spoke a bit of Hungarian, and Béla quickly learned to mix and match various expressions—he had also started learning English.
Finally, in May 1957, Béla and his family received their residence permits in Canada, and after a long journey, they moved to Saskatoon. He attended the local school, where he faced difficulties at first; however, he quickly adjusted and became fluent in English.
I. Béla Barabás still keeps the first pocket knife he received as a child in his family, and he was able to recreate the history of the photo from the aircraft carrier with the help of old newspapers. Today, he writes articles in English about the 1956 revolution and Hungarian history, sharing the story of solidarity that became a global symbol during those difficult months.
Author: Ádám Kolozsi
The Weekly Fortepan blog is a professional collaboration with the Capa Centre. The original article can be found HERE.
Read also:
On this October 23rd there is real hope for Hungary. The first poll was released that shows that Tisza is the most popular party in Hungary and is now ahead of Fidesz. There is real hope for change to end this corrupt regime that has brought Russian control back to Hungary and made Hungarians fearful of voicing their opposition to the regime due to state directed oppression. Hungary will come out of the dark and will be liberated in 2026! The days of Orban’s dictatorship are now numbered.